Article by UF/IFAS Extension Broward County Urban Horticulture Agent Lorna Bravo
Why is Sustainable Urban Food Production Important?
Globally, more than half of the population is living in urban areas that rely upon external supplies of resources, such as food and clean water. It is projected that 2.5 billion more people will live on the planet by the mid-21st century, with disproportionate growth in urban populations. The state of Florida, as the third most populous state, has reached a population of more than 21 million in 2018 and is a project to exceed 31 million in 2050.

Exploring New Sustainability Pathways
It is vital to explore sustainability pathways that enhance resource efficiency in urban systems, reduce tradeoffs, and improve urban resilience. Urban food production, by promoting local food production, decentralizing food supply, and reducing food imports from highly industrialized production systems, is one of such pathways that could contribute to long-term urban sustainability.
Did you know that 15% of the world’s food is grown in urban areas?
From backyard community gardens to vacant lots, and along highways and on rooftops, urban farmers are bringing people closer to their food in limited spaces. Data Source: USDA.
What is Sustainability?
The concept of sustainability is defined as the practice or development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs. Sustainability has three pillars or dimensions: environment, economics, and society, and thus achieving sustainability involves the balance of all these three goals simultaneously.
How Does Urban Food Production Contribute to Sustainability?
At the local scale, urban food production could achieve multi functionalities such as food security, water, and nutrient reuse, stormwater management, ecosystem health, and social-economic benefits (e.g., household income supplements, providing employment, and diversifying industry base). At regional to global scales, urban food production could counteract indirect land-use changes and promote climate mitigations through reducing environmental externalities (e.g., reduced greenhouse emissions and energy use associated with food supply chains) related to food trade and imports.
Interested in Urban Food Production in South Florida?
Incipient grass-root and business interests have advocated for different forms of urban food production (e.g., community garden, urban-adjacent farm, food forests, greenhouse production, vertical farming) across south Florida. (see figure below on selected representative sites)


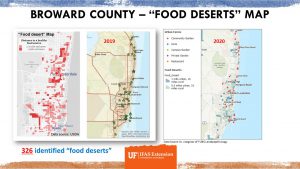
Food Desert Areas
Developing local food production is particularly relevant for south Florida, where food security is now becoming a significant concern with 326 identified “food deserts” areas. Food Desert areas are places where residents have difficulty in accessing affordable, fresh, and nutritious food.
What is The Sustainable Urban Food Production Short-Course?
This comprehensive UF/IFAS Extension short course includes lectures, hands-on workshops, and field trips. The course focuses on sustainable urban food production.

Who can register?
It is geared for anyone (e.g., community gardeners, urban farmers, homeowners, school teachers, entrepreneurs, general public) interests in increasing knowledge and awareness and adopting best management practices related to urban food production, and enhancing the livelihoods of urban residents.
Registration:
Interested in registering for the 2025 Course? Contact us
- Email our Urban Horticulture team:
Lorna Bravo: lbravo1@ufl.edu,
Follow us via Social Media
You can follow our Facebook page at @http://facebook.com/urbanhortbroward
Visit our Website@ http://sfyl.ifas.ufl.edu/broward/urban-horticulture/
Visit our YouTube Channel at https://tinyurl.com/urbanhhortbcyoutube
Our Twitter page: https://twitter.com/HortUrban
Our Instagram page:@urbanhortbroward
 0
0
